.svg)

- 适用于 JDK 24 的 GraalVM(最新)
- 适用于 JDK 25 的 GraalVM(早期访问)
- 适用于 JDK 21 的 GraalVM
- 适用于 JDK 17 的 GraalVM
- 存档
- 开发构建

Insight 手册
GraalVM Insight 是一款多功能、灵活的工具,用于编写可靠的应用程序。该工具的动态特性使您能够选择性地在现有应用程序上应用追踪切入点,而不会损失性能。
任何中等技能的开发者都可以轻松创建所谓的 Insight 代码片段,并动态地将其应用于实际应用程序。这提供了对程序执行和行为的终极洞察,而不会影响其速度。
目录 #
- 快速入门
- 热点前 10 名示例
- 将 Insight 应用于任何 GraalVM 语言
- 使用 JavaScript 进行 Insight
- 使用 Python 进行 Insight
- 使用 Ruby 进行 Insight
- 使用 R 进行 Insight
- C 代码的 Insight
- 检查值
- 修改局部变量
- 特定位置的 Insight
- 在 Node.JS 中延迟 Insight 初始化
- 处理异常
- 拦截并修改执行
- 最小开销
- 访问局部变量时的最小开销
- 访问执行栈
- 关于 GraalVM Insight API 的说明
- 堆转储
快速入门 #
从一个经典的 HelloWorld 示例开始。创建一个名为 source-tracing.js 的脚本,内容如下:
insight.on('source', function(ev) {
if (ev.characters) {
print(`Loading ${ev.characters.length} characters from ${ev.name}`);
}
});
使用 GraalVM 的 node 启动器运行它,并添加 --insight 工具选项。观察加载和评估的脚本:
./bin/node --js.print --experimental-options --insight=source-tracing.js -e "print('The result: ' + 6 * 7)" | tail -n 10
Loading 29938 characters from url.js
Loading 345 characters from internal/idna.js
Loading 12642 characters from punycode.js
Loading 33678 characters from internal/modules/cjs/loader.js
Loading 13058 characters from vm.js
Loading 52408 characters from fs.js
Loading 15920 characters from internal/fs/utils.js
Loading 505 characters from [eval]-wrapper
Loading 29 characters from [eval]
The result: 42
刚才发生了什么?GraalVM Insight 的 source-tracing.js 脚本使用了提供的 insight 对象,将一个源监听器附加到运行时。因此,每当 node 加载一个脚本时,监听器就会收到通知,并可以执行一个操作(在本例中,是打印已处理脚本的长度和名称)。
热点前 10 名示例 #
收集洞察信息不仅限于打印语句。您可以使用您的语言执行任何图灵完备的计算。例如,一个程序可以在执行结束后统计所有方法调用,并转储最常用的那些。
将以下代码保存到 function-hotness-tracing.js:
var map = new Map();
function dumpHotness() {
print("==== Hotness Top 10 ====");
var count = 10;
var digits = 3;
Array.from(map.entries()).sort((one, two) => two[1] - one[1]).forEach(function (entry) {
var number = entry[1].toString();
if (number.length >= digits) {
digits = number.length;
} else {
number = Array(digits - number.length + 1).join(' ') + number;
}
if (count-- > 0) print(`${number} calls to ${entry[0]}`);
});
print("========================");
}
insight.on('enter', function(ev) {
var cnt = map.get(ev.name);
if (cnt) {
cnt = cnt + 1;
} else {
cnt = 1;
}
map.set(ev.name, cnt);
}, {
roots: true
});
insight.on('close', dumpHotness);
map 是整个 Insight 脚本可见的全局变量,它使代码能够在 insight.on('enter') 函数和 dumpHotness 函数之间共享数据。后者在 node 进程执行结束时执行(通过 insight.on('close', dumpHotness) 注册)。运行程序:
./bin/node --js.print --experimental-options --insight=function-hotness-tracing.js -e "print('The result: ' + 6 * 7)"
The result: 42
==== Hotness Top 10 ====
516 calls to isPosixPathSeparator
311 calls to :=>
269 calls to E
263 calls to makeNodeErrorWithCode
159 calls to :anonymous
157 calls to :program
58 calls to getOptionValue
58 calls to getCLIOptionsFromBinding
48 calls to validateString
43 calls to hideStackFrames
========================
当 node 进程退出时,会打印出一个包含函数调用名称和计数的表格。
将 Insight 应用于任何 GraalVM 语言 #
前面的示例是用 JavaScript 编写的,并使用了 node,但由于 GraalVM 的多语言特性,您可以将相同的工具应用于 GraalVM 支持的任何语言。例如,使用 GraalVM Insight 测试 Ruby 语言。
首先,在 source-trace.js 文件中创建该工具:
insight.on('source', function(ev) {
if (ev.uri.indexOf('gems') === -1) {
let n = ev.uri.substring(ev.uri.lastIndexOf('/') + 1);
print('JavaScript instrument observed load of ' + n);
}
});
在 helloworld.rb 文件中准备您的 Ruby 程序:
puts 'Hello from GraalVM Ruby!'
注意:请确保已启用 Ruby 支持。请参阅多语言编程指南。
将 JavaScript 工具应用于 Ruby 程序。您应该会看到以下内容:
./bin/ruby --polyglot --insight=source-trace.js helloworld.rb
JavaScript instrument observed load of helloworld.rb
Hello from GraalVM Ruby!
有必要使用 --polyglot 参数启动 GraalVM 的 Ruby 启动器,因为 source-tracing.js 脚本仍然是用 JavaScript 编写的。
使用 JavaScript 进行 Insight #
如前一节所述,GraalVM Insight 不限于 Node.js。它适用于 GraalVM 提供的所有语言运行时。尝试 GraalVM 自带的 JavaScript 实现。
创建 function-tracing.js 脚本:
var count = 0;
var next = 8;
insight.on('enter', function(ev) {
if (count++ % next === 0) {
print(`Just called ${ev.name} as ${count} function invocation`);
next *= 2;
}
}, {
roots: true
});
在 sieve.js 上运行它。这是一个示例脚本,它使用埃拉托斯特尼筛法的一种变体来计算十万个素数:
./bin/js --insight=function-tracing.js sieve.js | grep -v Computed
Just called :program as 1 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 17 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 33 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 65 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 129 function invocation
Just called Filter as 257 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 513 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 1025 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 2049 function invocation
Just called Natural.next as 4097 function invocation
使用 Python 进行 Insight #
不仅可以检测任何 GraalVM 语言,而且 Insight 脚本也可以用该语言编写。在本节中,您将找到一个 Python 示例。
可以用 Python 编写 GraalVM Insight 脚本。此类 Insight 可应用于用 Python 或任何其他语言编写的程序。
以下脚本示例在调用 minusOne 函数时打印变量 n 的值。将此代码保存到 agent.py 文件:
def onEnter(ctx, frame):
print(f"minusOne {frame.n}")
class At:
sourcePath = ".*agent-fib.js"
class Roots:
roots = True
at = At()
rootNameFilter = "minusOne"
insight.on("enter", onEnter, Roots())
此代码使用 GraalVM 22.2 中引入的源位置声明式规范。对于较旧的 GraalVM 版本,请使用动态 sourceFilter:
def onEnter(ctx, frame):
print(f"minusOne {frame.n}")
class Roots:
roots = True
rootNameFilter = "minusOne"
def sourceFilter(self, src):
return src.name == "agent-fib.js"
insight.on("enter", onEnter, Roots())
使用以下命令将此脚本应用于 agent-fib.js:
`./bin/js --polyglot --insight=agent.py agent-fib.js`
注意:请确保已启用 Python 支持。请参阅多语言编程指南。
使用 Ruby 进行 Insight #
可以用 Ruby 编写 GraalVM Insight 脚本。此类 Insight 可应用于用 Ruby 或任何其他语言编写的程序。
注意:请确保已启用 Ruby 支持。请参阅多语言编程指南。
创建 source-tracing.rb 脚本:
puts("Ruby: Insight version #{insight.version} is launching")
insight.on("source", -> (env) {
puts "Ruby: observed loading of #{env.name}"
})
puts("Ruby: Hooks are ready!")
启动一个 Node.js 程序并使用 Ruby 脚本对其进行检测:
./bin/node --js.print --experimental-options --polyglot --insight=source-tracing.rb agent-fib.js
Ruby: Initializing GraalVM Insight script
Ruby: Hooks are ready!
Ruby: observed loading of node:internal/errors
Ruby: observed loading of node:internal/util
Ruby: observed loading of node:events
....
Ruby: observed loading of node:internal/modules/run_main
Ruby: observed loading of <...>/agent-fib.js
Three is the result 3
要跟踪变量值,请创建 agent.rb 脚本:
insight.on("enter", -> (ctx, frame) {
puts("minusOne #{frame.n}")
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: "minusOne",
at: {
sourcePath: ".*agent-fib.js"
}
})
此代码使用 GraalVM 22.2 中引入的源位置声明式规范。对于较旧的 GraalVM 版本,请使用动态 sourceFilter:
insight.on("enter", -> (ctx, frame) {
puts("minusOne #{frame.n}")
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: "minusOne",
sourceFilter: -> (src) {
return src.name == Dir.pwd+"/agent-fib.js"
}
})
上述 Ruby 脚本示例在调用 agent-fib.js 程序中的 minusOne 函数时,打印变量 n 的值:
./bin/node --js.print --experimental-options --polyglot --insight=agent.rb agent-fib.js
minusOne 4
minusOne 3
minusOne 2
minusOne 2
Three is the result 3
使用 R 进行 Insight #
同样的工具也可以用 R 语言编写。
创建 agent-r.R 脚本:
cat("R: Initializing GraalVM Insight script\n")
insight@on('source', function(env) {
cat("R: observed loading of ", env$name, "\n")
})
cat("R: Hooks are ready!\n")
使用它来追踪 test.R 程序:
./bin/Rscript --insight=agent-r.R test.R
R: Initializing GraalVM Insight script
R: Hooks are ready!
R: observed loading of test.R
唯一的改变是 R 语言。所有其他 GraalVM Insight 功能和 API 保持不变。
C 代码的 Insight #
不仅可以解释动态语言,而且借助 GraalVM 的 LLI 实现,您甚至可以混入用 C、C++、Fortran、Rust 等语言编写的静态编译程序。
例如,以一个长时间运行的程序 sieve.c 为例,它在 main 方法中包含一个永不结束的 for 循环。您可能希望为其设置一些执行配额。
首先,在 GraalVM 上执行该程序:
export TOOLCHAIN_PATH=`.../bin/lli --print-toolchain-path`
${TOOLCHAIN_PATH}/clang agent-sieve.c -lm -o sieve
./bin/lli sieve
GraalVM clang 包装器会添加特殊选项,指示常规 clang 将 LLVM 位码信息与正常本机代码一起保存在 sieve 可执行文件中。然后,GraalVM 的 lli 解释器可以使用位码全速解释程序。顺便说一下,比较通过 ./sieve 直接本机执行的结果和 ./bin/lli sieve 的解释器速度。对于解释器而言,它应该会显示出相当不错的结果。
现在,着重于打破无限循环。您可以使用此 JavaScript agent-limit.js Insight 脚本来完成:
var counter = 0;
insight.on('enter', function(ctx, frame) {
if (++counter === 1000) {
throw `GraalVM Insight: ${ctx.name} method called ${counter} times. enough!`;
}
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'nextNatural'
});
该脚本统计 C 语言 nextNatural 函数的调用次数,当函数被调用一千次时,它会发出一个错误以停止 sieve 的执行。运行程序,如下所示:
./bin/lli --polyglot --insight=agent-limit.js sieve
Computed 97 primes in 181 ms. Last one is 509
GraalVM Insight: nextNatural method called 1000 times. enough!
at <js> :anonymous(<eval>:7:117-185)
at <llvm> nextNatural(agent-sieve.c:14:186-221)
at <llvm> nextPrime(agent-sieve.c:74:1409)
at <llvm> measure(agent-sieve.c:104:1955)
at <llvm> main(agent-sieve.c:123:2452)
可以从本机代码访问基本局部变量。将上述 Insight 脚本替换为:
insight.on('enter', function(ctx, frame) {
print(`found new prime number ${frame.n}`);
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: (n) => n === 'newFilter'
});
每次将新素数添加到筛选列表中时打印一条消息:
./bin/lli --polyglot --insight=agent-limit.js sieve | head -n 3
found new prime number 2
found new prime number 3
found new prime number 5
lli、多语言和 GraalVM Insight 的结合为本机程序的追踪、控制以及交互式或批处理调试带来了巨大的可能性。
检查值 #
GraalVM Insight 不仅允许您追踪程序执行的位置,还提供了在执行期间访问局部变量和函数参数的值的能力。例如,可以编写一个工具来显示函数 fib 中参数 n 的值:
insight.on('enter', function(ctx, frame) {
print('fib for ' + frame.n);
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'fib'
});
此工具使用第二个函数参数 frame 来访问每个被检测函数内部的局部变量值。上述 Insight 脚本还使用 rootNameFilter,将其挂钩仅应用于名为 fib 的函数:
function fib(n) {
if (n < 1) return 0;
if (n < 2) return 1;
else return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
}
print("Two is the result " + fib(3));
当工具存储在 fib-trace.js 文件中,实际代码存储在 fib.js 中时,然后调用以下命令会产生有关程序执行以及函数调用之间传递的参数的详细信息:
./bin/node --js.print --experimental-options --insight=fib-trace.js fib.js
fib for 3
fib for 2
fib for 1
fib for 0
fib for 1
Two is the result 2
总结本节,GraalVM Insight 是一个用于多语言、与语言无关的面向切面编程的有用工具。
修改局部变量 #
GraalVM Insight 不仅可以访问局部变量,还可以修改它们。例如,以下是一个求数组和的程序:
function plus(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
var sum = 0;
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9].forEach((n) => sum = plus(sum, n));
print(sum);
它会打印出数字 45。应用以下 Insight 脚本,在添加非偶数之前“清除”它们:
insight.on('enter', function zeroNonEvenNumbers(ctx, frame) {
if (frame.b % 2 === 1) {
frame.b = 0;
}
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'plus'
});
当使用 js --insight=erase.js sumarray.js 启动时,只有值 20 会被打印出来。
GraalVM Insight 的 enter 和 return 挂钩只能修改现有变量。它们不能引入新变量。尝试这样做会引发异常。
特定位置的 Insight #
要获取特定代码位置的变量,at 对象可能不仅包含以下强制性源规范之一:具有匹配源文件路径的正则表达式的 sourcePath 属性,或具有源 URI 字符串表示的 sourceURI 属性。还可以指定可选的 line 和/或 column。我们以 distance.js 源文件为例:
(function(x, y) {
let x2 = x*x;
let y2 = y*y;
let d = Math.sqrt(x2 + y2);
for (let i = 0; i < d; i++) {
// ...
}
return d;
})(3, 4);
然后我们可以应用以下 distance-trace.js Insight 脚本来获取变量的值:
insight.on('enter', function(ctx, frame) {
print("Squares: " + frame.x2 + ", " + frame.y2);
}, {
statements: true,
at: {
sourcePath: ".*distance.js",
line: 4
}
});
insight.on('enter', function(ctx, frame) {
print("Loop var i = " + frame.i);
}, {
expressions: true,
at: {
sourcePath: ".*distance.js",
line: 5,
column: 21
}
});
这将给出:
./bin/js --insight=distance-trace.js distance.js
Squares: 9, 16
Loop var i = 0
Loop var i = 1
Loop var i = 2
Loop var i = 3
Loop var i = 4
Loop var i = 5
在 Node.JS 中延迟 Insight 初始化 #
GraalVM Insight 可以在任何 GraalVM 语言运行时中使用,包括 node 实现。然而,在 node 中,您可能不想编写普通的 Insight 脚本。您可能希望充分利用 node 生态系统的强大功能,包括其模块。以下是一个实现此功能的示例 agent-require.js 脚本:
let initialize = function (require) {
let http = require("http");
print(`${typeof http.createServer} http.createServer is available to the agent`);
}
let waitForRequire = function (event) {
if (typeof process === 'object' && process.mainModule && process.mainModule.require) {
insight.off('source', waitForRequire);
initialize(process.mainModule.require.bind(process.mainModule));
}
};
insight.on('source', waitForRequire, { roots: true });
Insight 脚本会尽快初始化,但在那个时刻 require 函数尚未准备好。因此,脚本首先在已加载脚本上附加一个监听器,当主用户脚本被加载时,它获取其 process.mainModule.require 函数。然后它使用 insight.off 移除探针,并调用实际的 initialize 函数来执行真正的初始化,同时可以访问所有 Node 模块。该脚本可以通过以下方式运行:
./bin/node --js.print --experimental-options --insight=agent-require.js yourScript.js
已知此初始化序列适用于使用主 yourScript.js 参数启动的 GraalVM node 12.10.0 版本。
处理异常 #
GraalVM Insight 工具可以抛出异常,这些异常随后会传播到周围的用户脚本。假设您有一个程序 seq.js 记录各种消息:
function log(msg) {
print(msg);
}
log('Hello GraalVM Insight!');
log('How');
log('are');
log('You?');
您可以注册一个工具 term.js,并根据观察到的日志消息,在 seq.js 程序的中间停止执行:
insight.on('enter', (ev, frame) => {
if (frame.msg === 'are') {
throw 'great you are!';
}
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'log'
});
term.js 工具等待对 log 函数的调用,并带有消息 are,在那一刻,它会发出自己的异常,从而有效地中断用户程序执行。结果如下:
./bin/js --polyglot --insight=term.js seq.js
Hello GraalVM Insight!
How
great you are!
at <js> :=>(term.js:3:75-97)
at <js> log(seq.js:1-3:18-36)
at <js> :program(seq.js:7:74-83)
Insight 工具发出的异常被视为常规语言异常。seq.js 程序可以使用常规的 try { ... } catch (e) { ... } 块来捕获它们,并像处理常规用户代码发出的异常一样处理它们。
拦截并修改执行 #
GraalVM Insight 能够修改程序的执行。它可以跳过某些计算并用自己的替代方案替换它们。以下面的 plus 函数为例:
function plus(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
改变 plus 方法的行为很容易。以下 Insight 脚本通过使用 ctx.returnNow 功能,将 + 运算替换为乘法运算:
insight.on('enter', function(ctx, frame) {
ctx.returnNow(frame.a * frame.b);
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'plus'
});
returnNow 方法会立即停止执行并返回到 plus 函数的调用者。plus 方法的主体根本不会执行,因为 Insight 的 on('enter', ...) 在函数实际主体执行之前就已应用。用乘法代替加法可能听起来不太吸引人,但相同的方法在为重复函数调用提供附加缓存(例如,记忆化)方面非常有用。
也可以让原始函数代码运行,只修改其结果。例如,将 plus 函数的结果始终修改为非负数:
insight.on('return', function(ctx, frame) {
let result = ctx.returnValue(frame);
ctx.returnNow(Math.abs(result));
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'plus'
});
Insight 挂钩在 plus 函数返回时执行,并使用 returnValue 辅助函数从当前的 frame 对象获取计算出的返回值。然后它可以修改该值,returnNow 会返回一个新结果。returnValue 函数始终在提供的 ctx 对象上可用,但只有在 on('return', ...) 挂钩中使用时,它才返回有意义的值。
最小开销 #
如果您问 GraalVM Insight 在应用脚本时是否会造成任何性能开销,答案是“否”或“最小”。开销取决于您的脚本所做的工作。如果它们在您的整个代码库中添加和传播复杂计算,那么您将为这些计算付出代价。然而,那将是您代码的开销,而不是检测的开销。使用一个简单的 function-count.js 脚本来测量开销。
var count = 0;
function dumpCount() {
print(`${count} functions have been executed`);
}
insight.on('enter', function(ev) {
count++;
}, {
roots: true
});
insight.on('close', dumpCount);
在一个迭代五十次的 sieve.js 示例上使用该脚本,该示例使用埃拉托斯特尼筛法的一种变体来计算十万个素数。重复计算五十次使运行时有机会预热并进行适当优化。以下是最佳运行结果:
./bin/js sieve.js | grep -v Computed
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 75 ms
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 73 ms
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 73 ms
现在将其与启用 GraalVM Insight 脚本时的执行时间进行比较:
./bin/js --insight=function-count.js sieve.js | grep -v Computed
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 74 ms
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 74 ms
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 75 ms
72784921 functions have been executed
差异是 2 毫秒。GraalVM Insight 融合了程序代码和 Insight 收集脚本之间的差异,使所有代码协同工作。count++ 调用在代表程序函数 ROOT 的所有位置都成为程序的自然组成部分。
访问局部变量时的最小开销 #
GraalVM Insight 代码在访问局部变量时,与定义它们的实际函数代码融为一体,没有明显的减速。
这可以通过以下 sieve.js 算法来演示,该算法计算十万个素数。它将找到的素数保存在通过以下函数构造的链表中:
function Filter(number) {
this.number = number;
this.next = null;
this.last = this;
}
首先,通过调用计算五十次并测量完成最后一轮所需的时间来测试其行为:
./bin/js -e "var count=50" --file sieve.js | grep Hundred | tail -n 1
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 73 ms
然后,通过观察每个新素数槽的分配来“测试”系统,例如,对 new Filter 构造函数的调用:
var sum = 0;
var max = 0;
insight.on('enter', (ctx, frame) => {
sum += frame.number;
if (frame.number > max) {
max = frame.number;
}
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'Filter'
});
insight.on('return', (ctx, frame) => {
log(`Hundred thousand prime numbers from 2 to ${max} has sum ${sum}`);
sum = 0;
max = 0;
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'measure'
});
每次分配 new Filter(number) 时,都会捕获 number 的最大值(例如,找到的最高素数),以及到目前为止找到的所有素数的 sum。当 measure 中的主循环结束时(意味着有十万个素数),结果会被打印出来。
现在尝试以下操作:
./bin/js -e "var count=50" --insight=sieve-filter1.js --file sieve.js | grep Hundred | tail -n 2
Hundred thousand prime numbers from 2 to 1299709 has sum 62260698721
Hundred thousand prime numbers in 74 ms
根本没有减速。GraalVM Insight 与 GraalVM 编译器的内联算法结合使用时,能够提供强大的检测功能,几乎没有性能损失。
访问执行栈 #
GraalVM Insight 有一种方法可以访问整个执行栈。以下代码片段展示了如何实现这一点:
insight.on("return", function(ctx, frame) {
print("dumping locals");
ctx.iterateFrames((at, vars) => {
for (let p in vars) {
print(` at ${at.name} (${at.source.name}:${at.line}:${at.column}) ${p} has value ${vars[p]}`);
}
});
print("end of locals");
}, {
roots: true
});
每当 Insight 挂钩被触发时,它会打印当前执行栈,包括函数的 name、source.name、line 和 column。此外,它还会打印每个帧中所有局部 vars 的值。还可以通过将新值赋给现有变量来修改它们的值:vars.n = 42。访问整个栈是灵活的,但与访问当前执行帧中的局部变量不同,这不是一项快速操作,如果您希望程序继续全速运行,请明智使用。
堆转储 #
GraalVM Insight 可用于在执行期间对程序堆的某个区域进行快照。将 --heap.dump=/path/to/output.hprof 选项与常规的 --insight 选项一起使用。Insight 脚本将获得对带有 dump 函数的 heap 对象的访问权限。在需要时放置您的挂钩,并在适当的时候转储堆:
insight.on('return', (ctx, frame) => {
heap.dump({
format: '1.0',
depth: 50, // set max depth for traversing object references
events: [
{
stack : [
{
at : ctx, // location of dump sieve.js:73
frame : {
// assemble frame content as you want
primes : frame.primes, // capture primes object
cnt : frame.cnt, // capture cnt value
},
depth : 10 // optionally override depth to ten references
}, // there can be more stack elements like this one
]
},
// there can be multiple events like the previous one
],
});
throw 'Heap dump written!';
}, {
roots: true,
rootNameFilter: 'measure'
});
将此代码片段保存为 dump.js 文件。获取 sieve.js 文件并如下启动它:
./bin/js --insight=dump.js --heap.dump=dump.hprof --file sieve.js
一个 dump.hprof 文件将在 measure 函数结束时创建,捕获您的程序内存状态。使用常规工具(如 VisualVM 或 NetBeans)检查生成的 .hprof 文件:
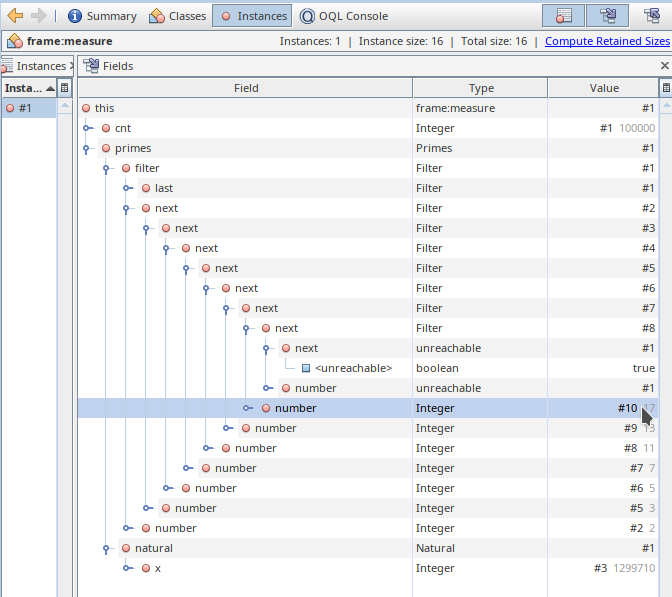
上图显示了在 sieve.js 脚本中 measure 函数结束时进行的堆转储。该函数刚刚计算了十万个素数(数量在变量 cnt 中可用)。图中显示了一个 Filter 链表,其中包含从 2 到 17 的素数。链表的其余部分被隐藏在 unreachable 对象后面(仅请求了深度为 10 的引用)。最后一个变量 x 显示了计算所有素数所搜索的自然数数量。
堆转储缓存 #
为了加快堆转储过程并优化生成的转储,可以启用内存缓存。属性在转储到缓存之间未更改的对象只存储一次,从而减小了生成的堆转储大小。添加(例如)--heap.cacheSize=1000 选项以使用 1000 个事件的内存缓存。默认情况下,缓存会在满时转储到文件并清除。该策略可以通过 --heap.cacheReplacement=lru 选项更改,该选项在达到缓存大小限制时,保留最近的转储事件并丢弃最旧的事件。
要将缓存刷新到堆转储文件,需要显式调用 heap.flush()。
关于 GraalVM Insight API 的说明 #
通过 insight 对象公开的 GraalVM Insight API 的兼容性以兼容的方式实现。GraalVM Insight API 可通过此链接找到。insight 对象的属性和函数作为其 Javadoc 的一部分提供。
未来的版本将添加新功能,但一旦公开的功能将保持可用。如果您的脚本依赖于某些新功能,它可能会检查公开 API 的版本:
print(`GraalVM Insight version is ${insight.version}`);
API 中的新元素带有相关的 @since 标签,用于描述相关功能可用的最低版本。